Short script using cryosparc-tools to import ImageShifts from micrograph-associated .mdoc files. To use, fill out the variables at the top, and run this in the directory with the .mdoc files. It should make a new job in the specified workspace with an exposure output that you can then put into the Exposure Group Utilities job, and use to cluster via image shift.
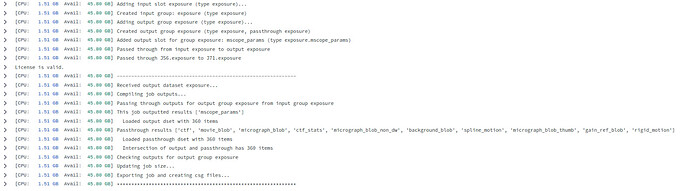
Example job:
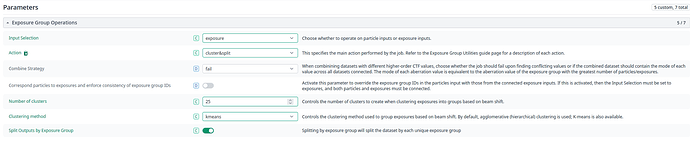
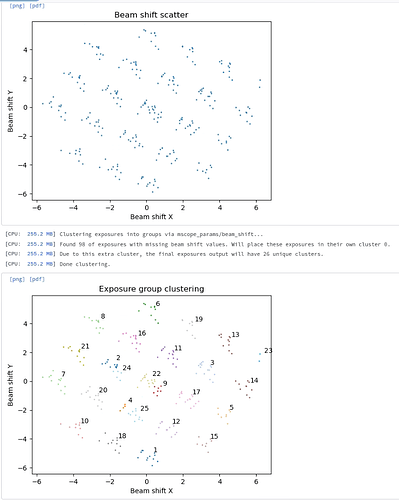
Exposure group utilities follow-up job:
(hopefully your shift groups look better - we were having hole centering issues on this dataset)
from pathlib import Path
import re
from cryosparc.tools import CryoSPARC
from getpass import getpass
##### Instructions #####
# Place a copy of this file in each directory you have .mdoc
# files in, load the cryosparc-tools conda environment (if using)
# and run this script: python3 cs_mdoc_image_shift.py
##### Variables #####
expected_groups = 25
cs_license = 'asdf1348-replace-me-123lkj12'
cs_hostname = 'mycryosparcinstance.mysupercoolinstitution.com'
cs_port = 39000
cs_email = 'myemail@mydomain.com'
cs_project = 'P83'
cs_workspace = 'W1'
cs_job = 'J56'
cs_job_output = 'exposure'
##### (il)Logic #####
#Set directory and get list of mdocs
mdoc_directory = Path(".")
mdoc_list = list(mdoc_directory.glob('**/*.mdoc'))
#Initialize list that will hold dictionary with exposure information
exposures = []
#Iterate through list of mdoc files
for i in range(len(mdoc_list)):
#Open individual mdoc file
with open(mdoc_list[i]) as mdoc:
#Read each line in mdoc file
for line in mdoc:
#if the line matches, store the name of the file and also the image shift values into a list
if re.search("ImageShift",line):
shift_data = {
"exposure": str(mdoc_list[i]).rsplit(sep='.',maxsplit = 1)[0],
"x_shift": line.rsplit()[2],
"y_shift": line.rsplit()[3],
}
exposures.append(shift_data)
#Get CS password
print("Please enter CryoSPARC password: ")
cs_password = getpass()
#Connect to CS
cs = CryoSPARC(license=cs_license, email=cs_email, password=cs_password, host=cs_hostname, base_port=cs_port)
assert cs.test_connection()
#Find dataset and copy it to a new dataset
project = cs.find_project(cs_project)
job = cs.find_job(cs_project, cs_job)
cs_exposures = job.load_output(cs_job_output)
grouped_exposures = cs_exposures.copy()
#For every row in the dataset, search entire mdoc data and see if it fits a known movie and image shift. There's probably a much faster way to do this.
for row in grouped_exposures.rows():
for i in range(len(exposures)):
if exposures[i]['exposure'] == row['movie_blob/path'].rsplit(sep='/')[-1]:
row['mscope_params/beam_shift'][0] = exposures[i]['x_shift']
row['mscope_params/beam_shift'][1] = exposures[i]['y_shift']
row['mscope_params/beam_shift_known'] = 1
break
#Make a new external job with the updated values, and passthrough the remaining, non-updated values
project.save_external_result(
workspace_uid=cs_workspace,
dataset=grouped_exposures,
type="exposure",
name="exposure",
slots=["mscope_params"],
passthrough=(cs_job,cs_job_output),
title="ImageShift Updated Exposures"
)